Introduction to Quality Control Dashboards
In today’s competitive manufacturing environment, quality is no longer a goal—it’s a necessity. Quality standards maintenance leads to customer satisfaction and decreased waste and production expenses and defends the corporate brand image. Quality control consistency between different processes and products proves to be more challenging than people think. The system needs to display data in real time while showing potential issues before they result in expensive problems. A quality control dashboard serves as an essential tool for this purpose.
A Quality Control Dashboard functions as a single reporting platform which unifies essential quality metrics into an easy-to-use visual interface. The system provides an organized display of essential performance indicators through a user-friendly interface which eliminates the need for paper reports and spreadsheet management and email communication. Manufacturers who establish proper dashboards can track product quality in real time to identify issues promptly which supports their organizational growth.
Why Quality Control Dashboards Are Essential
A quality control dashboard which is well constructed serves as a key element for achieving operational efficiency. The system allows stakeholders to track production metrics and detect patterns and respond immediately to problems that occur on the production floor. The automotive and pharmaceutical and electronics and food manufacturing industries need exact and fast quality data because their small production flaws create major operational issues.
Quality control dashboards provide users with data that goes past the standard tracking of defects and inspection results. The system operates as a decision support system which helps managers to identify main problems and assess operational performance between shifts and facilities and forecast future challenges. Real-time metric tracking enables organizations to maintain compliance with their internal standards and industry regulations and customer requirements. Dashboards function as fundamental instruments which help organizations reach their excellence targets.
Common Problems Without a QC Dashboard
Quality data management becomes disorganized because there is no dashboard to track it. Teams currently use manual tracking methods which include spreadsheets and email chains and handwritten logs. The independent systems create reporting and interpretation problems because they function as independent systems. The information available to decision-makers may be delayed or outdated or completely absent when it reaches them.
Moreover, when data is scattered across multiple systems and files, it’s nearly impossible to gain a holistic view of quality performance. The absence of visibility leads to delayed responses for quality problems and reactive choices and lost chances for betterment. The combination of these inefficiencies results in elevated rework rates and dissatisfied customers and decreased manufacturing operational performance.
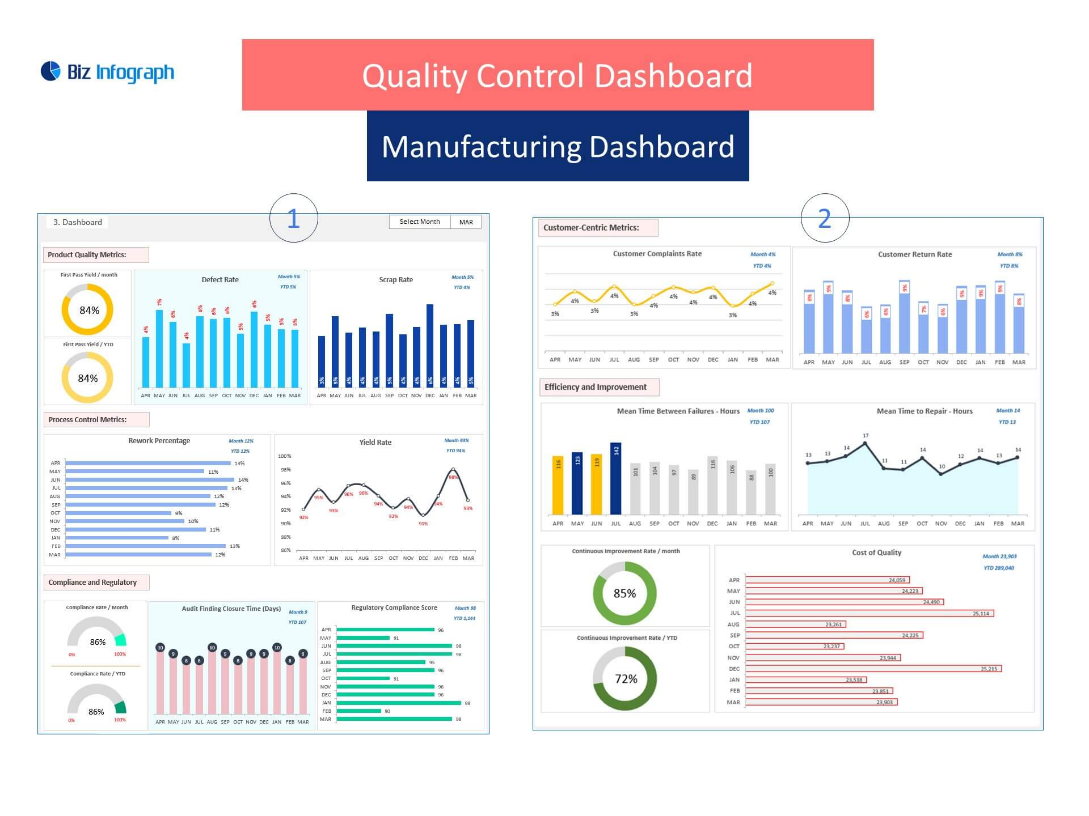
Defect Rate
Quality performance depends heavily on the fundamental indicator which is defect rate. The percentage of products that fail to meet production or inspection requirements is what this metric represents. Organizations use this metric to determine how often problems occur while monitoring if their frequency improves or deteriorates throughout time. A quality control dashboard that shows defect trends for products and production lines and time periods enables teams to detect issues fast so they can take corrective measures.
Inspection Results and Compliance Rates
Quality standards depend on the essential process of tracking product inspection results together with audit and compliance check outcomes. The dashboard displays inspection results through percentage metrics that show both successful inspections and failed inspections and required rework. All businesses operating in regulated sectors need compliance rates as their essential KPI measurement. Organizations can maintain their certifications and reduce regulatory noncompliance risks through dashboard implementation for tracking standard compliance based on ISO and FDA and customer requirements.
Excel-Based Dashboards
Small teams and new businesses tend to choose Excel as their dashboard development tool of choice. The platform provides users with flexibility and simple operation and broad accessibility. Users can perform various tasks in Excel by creating tables and inserting charts and applying conditional formatting and automating reports through macros or Power Query. Excel serves as an affordable entry-level tool for quality tracking although it does not support real-time data integration. The dashboards built in Excel support cross-department information sharing and users can personalize the dashboards according to their specific production line and product requirements.
Power BI or Tableau Dashboards
For larger teams or manufacturers managing high volumes of data, tools like Power BI and Tableau offer scalable solutions with advanced capabilities. The platforms integrate real-time data which allows dashboards to update automatically when new inspection or production data becomes available. These tools enable users to create advanced visualizations and interactive elements which include filtering capabilities and drilldown functionality and time-based comparison options. Organizations can convert their static data into real-time actionable information that reaches all parts of the organization through Power BI dashboard integration with ERP systems and MES and quality management systems.
Collect and Structure Quality Data
The first step requires collecting all required data which needs to be properly organized. The data collection process may involve inspection logs and test results and defect reports and audit scores. The data needs to follow an organizational structure that matches the KPIs which you want to monitor. The system requires each record to contain essential fields that include product ID and batch number and defect type and inspector name and timestamp and pass/fail status. A dashboard requires clean data which needs proper organization to function effectively.
Automate Data Refresh and Alerts
The dashboard system will automatically refresh its data on Power BI and Tableau platforms whenever new information enters the system. Linked tables or data connections in Excel-based solutions enable users to minimize their need for manual data update work. The system needs to have alert capabilities which will notify quality or production teams when any KPI hits predetermined threshold points. Organizations can use alerts to deliver fast responses while their staff members keep their work performance at optimal levels.
Involve the Quality and Production Teams
A dashboard achieves its highest value through precise data presentation which shows actual production floor activities. The quality assurance team and line supervisors and operators need to participate in establishing performance metrics and verifying data origin. The team feedback allows the dashboard to track important performance indicators which results in system adoption across the entire organization.
Review and Update Metrics Regularly
Business targets change over time because quality standards also undergo changes. Check the dashboard periodically to verify that the KPIs maintain their alignment with current strategic goals. Add new metrics when needed, retire outdated ones, and update visualizations to reflect current reporting needs. The dashboard continues to serve its purpose effectively because of regular improvement work.
Conclusion
The quality control dashboard functions as a strategic tool which enables manufacturing teams to maintain quality standards while detecting opportunities for improvement and controlling operational changes. The system allows teams to achieve shared goals through collaborative work while delivering transparent quality performance metrics. Bizinfograph offers ready-to-use dashboard templates on Finance, Sales, HR and Manufacturing.